Storage GUI
Creating a Storage GUI
To create a storage GUI subwindow:
Launch lys and open the
proc.pyfile (press Ctrl+P).Add the following code to define a class for the storage GUI subwindow and save it (press Ctrl+S).
from lys.widgets import LysSubWindow
from lys_instr import DataStorage, gui
class Window(LysSubWindow):
def __init__(self):
super().__init__()
storage = DataStorage()
storageGUI = gui.DataStorageGUI(storage)
self.setWidget(storageGUI)
self.adjustSize()
Calling Window() in the lys command line launches the GUI subwindow as follows:
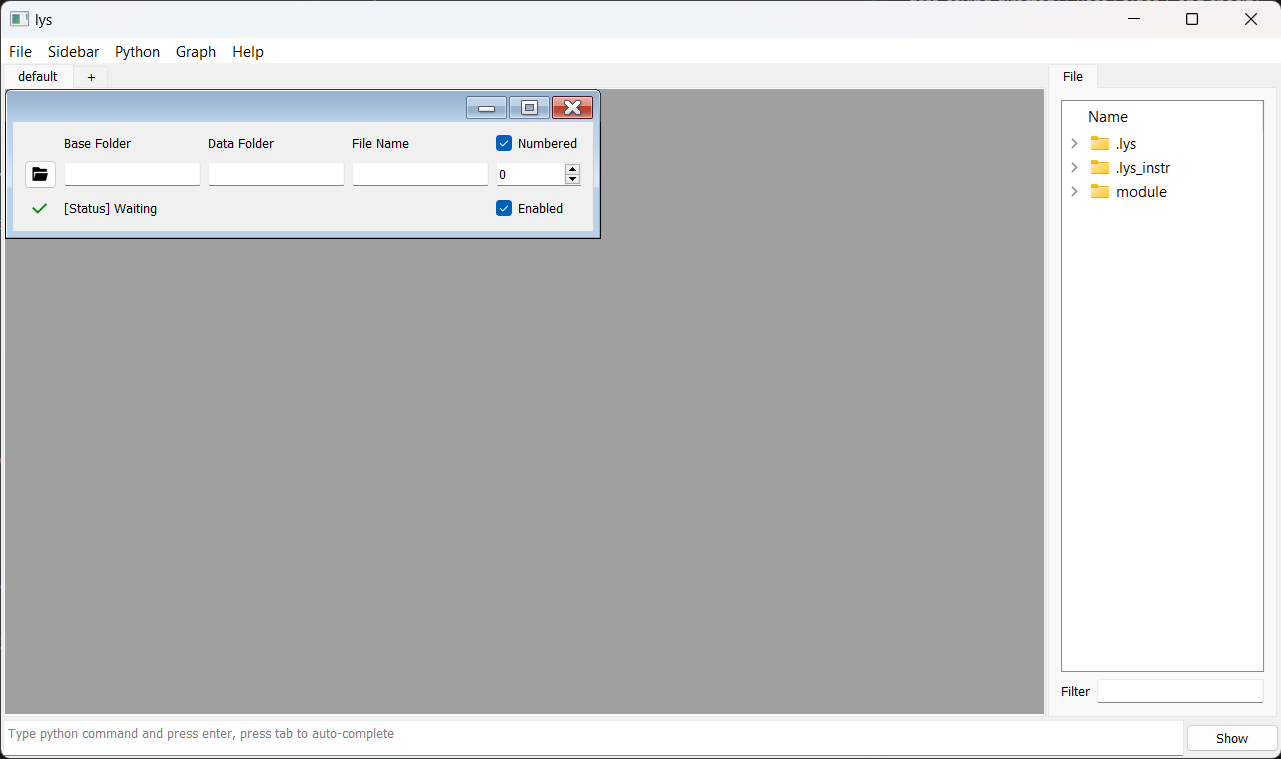
Click File (icon) to select the data-saving directory (“Base Folder”). By default, this is the directory from which you launched lys. You can enter a “Folder Name” and “File Name” (without extension) directly.
The “Enabled” checkbox toggles data saving on or off. The “Numbered” checkbox enables automatic numbering in file names: the number specified in the spin box is appended to the file name (e.g., “yourDataFolder/yourFileName_0.npz”, “yourDataFolder/yourFileName_1.npz”). Data is saved in NumPy ndarray format (.npz).
Connecting Storage to Detector
In practice, a storage is used to save data acquired by a detector.
Simply connecting a storage instance to a detector instance using the storage’s connect() method enables automated data saving.
Using the same detector instance as on the previous page, you can create a GUI for connected storage and detector:
from lys.widgets import LysSubWindow
from lys.Qt import QtWidgets
from lys_instr import DataStorage, dummy, gui
class Window(LysSubWindow):
def __init__(self):
super().__init__()
detector = dummy.MultiDetectorDummy(frameShape=(256, 256))
storage = DataStorage()
storage.connect(detector) # Connect storage to detector
detectorGUI = gui.MultiDetectorGUI(detector)
storageGUI = gui.DataStorageGUI(storage)
VBox = QtWidgets.QVBoxLayout() # Create a vertical box to hold the two GUIs
VBox.addWidget(storageGUI) # Add storage GUI to the box (upper)
VBox.addWidget(detectorGUI) # Add detector GUI to the box (lower)
w = QtWidgets.QWidget()
w.setLayout(VBox)
self.setWidget(w)
self.adjustSize()
The GUI layout is constructed using standard QtWidgets conventions (in the last 2-7 lines of the code above); you can ignore these details for now in this tutorial.
Calling Window() in the lys command line launches the combined GUI subwindow as follows:
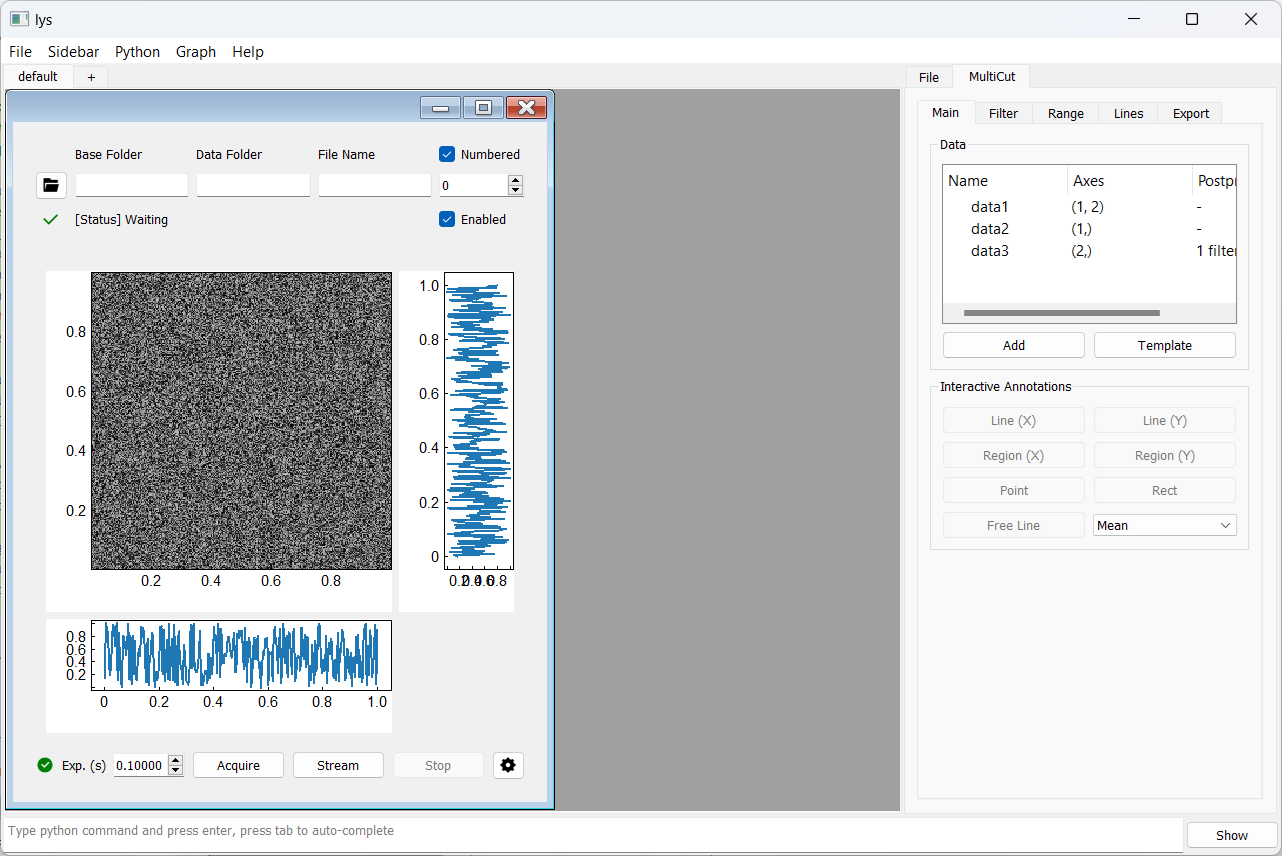
On each acquisition event, the storage instance automatically saves the acquired data to the specified path.
For real applications, you need to connect the data storage instance to a device-specific detector instance.