Axis Calibration and Dependency
Axis Calibration
In some cases, motor axis values require calibration.
The PreCorrection utility enables axis calibration using user-defined correction functions or data.
Suppose the motor axis “x” requires calibration, and the relationship between the raw position and the corrected position is given by a set of data points.
These data can be stored in a NumPy .npz file with the following structure:
Axis Dependency
PreCorrection also supports defining dependencies among axes.
Suppose the position of “y” must always follow a fixed function of “x”, for example, y = x/2 while only “x” is directly controlled.
A simple GUI combining a motor and a corrector can be constructed as follows:
from lys.widgets import LysSubWindow
from lys.Qt import QtWidgets
from lys_instr import PreCorrector, gui, dummy
from lys_instr.PreCorrection import _FunctionCombination, _InterpolatedFunction
class Window(LysSubWindow):
def __init__(self, parent=None):
super().__init__(parent)
self._motor = dummy.MultiMotorDummy("x", "y")
self._corrector = PreCorrector([self._motor])
self._initLayout()
self.adjustSize()
def _initLayout(self):
_motorGUI = gui.MultiMotorGUI(self._motor, axisNamesSettable=("x",), axisNamesJoggable=("x",)) # only enable "x" axis control
_correctorGUI = gui.PreCorrectorGUI(self._corrector)
self._tab = QtWidgets.QTabWidget()
self._tab.addTab(_motorGUI, "Motor")
self._tab.addTab(_correctorGUI, "PreCorr")
VBox = QtWidgets.QVBoxLayout()
VBox.addWidget(self._tab)
HBox = QtWidgets.QHBoxLayout()
HBox.addLayout(VBox)
w = QtWidgets.QWidget()
w.setLayout(HBox)
self.setWidget(w)
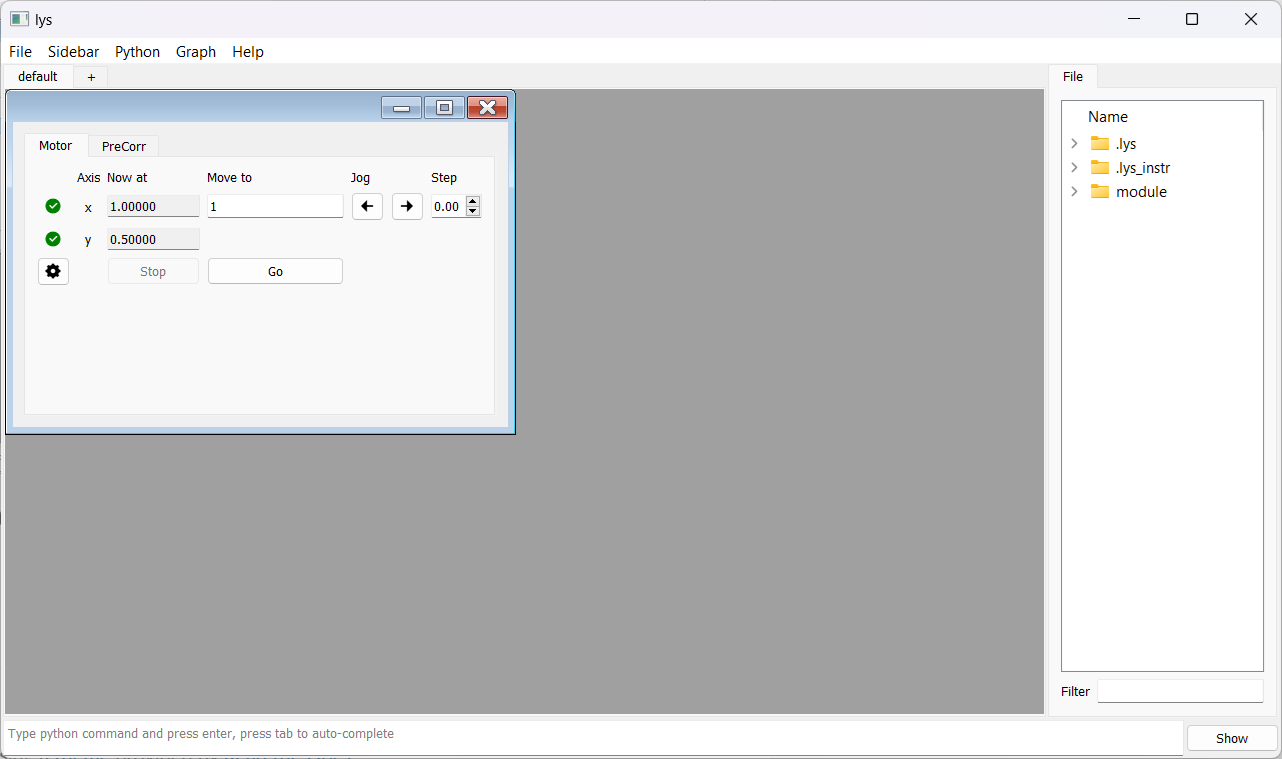
The resulting GUI appears as follows. Only the “x” axis is enabled for control:
In the PreCorr tab, right-click on the tree space and select “Add Target” to add a target axis, i.e., “y”.
Then, right-click on the target “y” and select “Add Variable”, choosing “x” as the dependency axis.
Next, double-click on the expression space of target “y” to enter x/2.
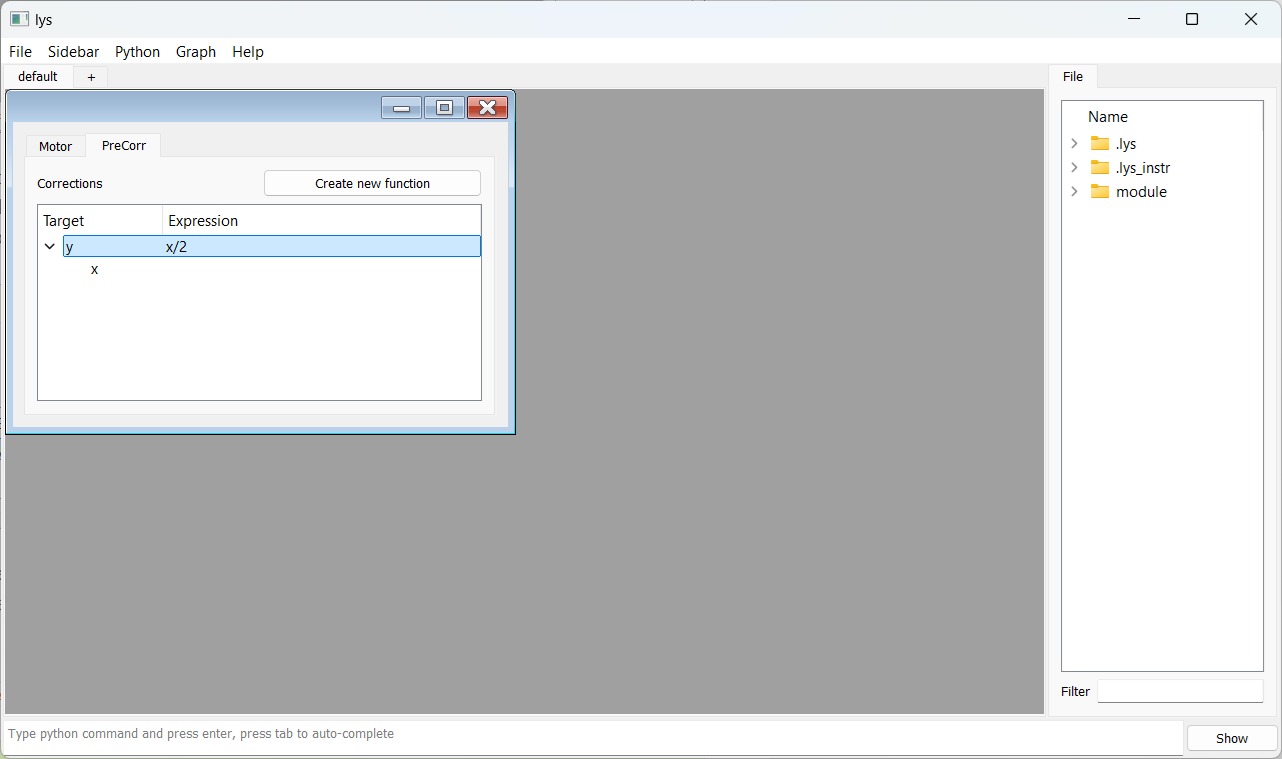
Now, when you enter a target position for “x” in the Motor tab and click Go, the motor will move “x” to the specified position and “y” will automatically be set to half of “x”.